 |
 |
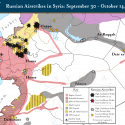
Russian Airstrikes in Syria: September 30 - October 14
By Genevieve Casagrande and Jodi Brignola
Key Takeaway: Russia’s involvement in Syria is facilitating ISIS’s territorial gains, while also strengthening Assad. Russia is supporting the Syrian regime’s offensives in Latakia, the al-Ghab Plain, and northern Hama. Russia also intensified strikes on rebel-held northwestern Aleppo, likely to set conditions for an imminent Russian-Iranian-Syrian regime offensive in the area. U.S. defense officials and local Syrian activists reported the arrival of hundreds of Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC)-Quds Force fighters and other Iranian proxy forces in Aleppo over the past few days. Russian strikes largely concentrated along the rebel-held supply route leading to the besieged regime enclaves of Nubl and Zahraa northwest of Aleppo City. If the regime can link with these enclaves, they will successfully sever the rebel-held supply route from Aleppo City to the Turkish border. Simultaneous regime offensives in both Hama and Aleppo Provinces will likely fix rebel forces along multiple fronts and prevent them from reinforcing their positions across northwestern Syria, resulting in a loss of terrain for the Syrian opposition.
ISIS is benefiting from Russia’s strikes on the Syrian opposition. On October 9, ISIS advanced 10 kilometers against rebels in northeastern Aleppo, the largest advance by ISIS in the province since August 2015. ISIS continued to conduct probing attacks against rebels northeast of Aleppo City from October 10-14. The Syrian regime and ISIS have historically leveraged one another’s offensives in order to advance against rebel forces in the northern Aleppo countryside. Both ISIS and the regime will likely capitalize on the effects of Russian airstrikes on rebels. Russian airstrikes have thus far failed to deter ISIS from launching new offensives and rather have facilitated ISIS’s seizure of new terrain.
The following graphic depicts ISW’s assessment of Russian airstrike locations based on reports from local Syrian activist networks, Syrian state-run media, and statements by Russian and Western officials.
High-Confidence reporting. ISW places high confidence in reports corroborated both by official government statements reported through credible channels and documentation from rebel factions or activist networks on the ground in Syria deemed to be credible.
Low-Confidence reporting. ISW places low confidence in secondary sources that have not been confirmed or sources deemed likely to contain disinformation.