|
 |
How We Got Here With Russia: The Kremlin's Worldview

March 2019
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
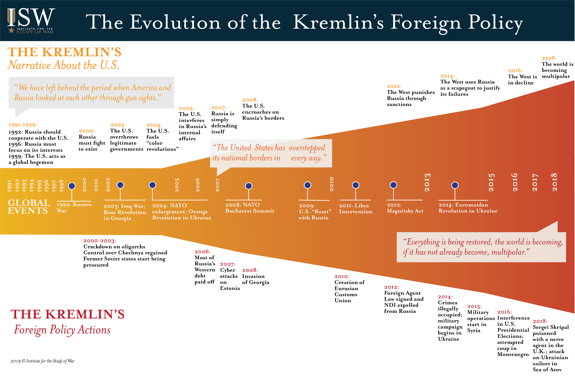
The Kremlin’s increasingly assertive foreign policy, including its illegal occupation of Crimea in 2014 and its intervention in Syria in 2015, came unexpectedly to many in the West. These events were nonetheless mere extensions of the worldview held by Russian President Vladimir Putin. This worldview was built on more than two decades of compounded dissatisfaction with the West as well as Putin’s cumulative experiences in his ongoing global campaigns to achieve his core objectives: the preservation of his regime, the end of American hegemony, and the reinstatement of Russia as a global power. Some of these ambitions were tamed, and others expedited, by external events, yet their core has remained the same and often at odds with the West. The U.S. believed that a brief period of non-assertive foreign policy from the mid-1980s to mid-1990s had become the new norm for Russia. This period was not the norm but an anomaly. Putin’s foreign policy has always been assertive, similar to Russia’s historic foreign policy. The U.S. may thus find itself once again surprised by Putin. This paper examines the evolution of Russia’s foreign policy worldview since the collapse of the Soviet Union to help understand the likely next priorities of the Kremlin.
INTRODUCTION
The U.S. has routinely attempted to reset relations with Russia since the rise to power of Russian President Vladimir Putin in 2000. The Soviet Union’s collapse led legions of scholars and policy-makers to pivot towards the new issues of a post-Soviet Middle East, Europe, and Asia. An entire generation of Americans hardly thought about Russia. The Russian Federation was seen as a former foe that could be integrated - albeit uneasily - into the international system led by the U.S.
Yet Russia did not view the slate as clean. The Kremlin’s foreign policy narrative, by contrast, soon focused on America’s disregard for its interests and the need to achieve a multipolar international system free of U.S. hegemony. Putin has remained clear on these goals since his ascent to the Kremlin. Russia needed to recover from its weakened state, reestablish itself as a global power, and achieve a new world order that held up the Kremlin as an equal - not a dependent - to the U.S.
Click image to enlarge.
Putin’s twenty-year tenure in power has had a cumulative effect on his worldview. His assertiveness has grown in step with his strengthened grip on domestic power and his growing perception that he faces only limited international pushback. His personal resentment of geopolitical slights has grown and fed back into Russia’s national security dialogue. The influence of other forceful national security leaders has also grown. Putin has responded to internal challenges by seeking foreign policy distractions. The direction of his aims has always been consistent even if the vigor and rancor with which they are pursued has increased.