ISIS and Iranian-backed Militias Compete to Control Baghdad Region
May 6, 2021 - Eva Kahan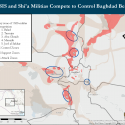
Key Takeaway: Iranian-backed militias are increasingly supplanting other Iraqi security forces and asserting control over Baghdad and surrounding areas, creating opportunities for ISIS to infiltrate Baghdad. Iranian-backed militias are also exerting control over populations and transit routes around Baghdad in hopes to eject US forces and set conditions to maintain a long-term demographic majority. Militia activity causes other Iraqi security forces to divide their attention between countering militias and countering ISIS, reducing the effectiveness of both efforts. ISIS is exploiting this gap to build durable support zones through the Baghdad Belts from which it can stage spectacular attacks. The Iraqi Security Forces must develop better local security strategies to more effectively counter both militia and ISIS campaigns in Baghdad and the Baghdad Belts.